Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Autoencoder-Based Recommenders
Last Updated: 29th January, 2026Denoising Autoencoders
Denoising Autoencoders (DAEs) are neural networks trained to reconstruct original input data from a corrupted version. In recommender systems, this means learning to predict missing ratings or preferences from partially observed data. The model is fed with a user’s incomplete interaction vector (e.g., watched movies) and trained to reconstruct the full vector, effectively predicting unseen preferences.
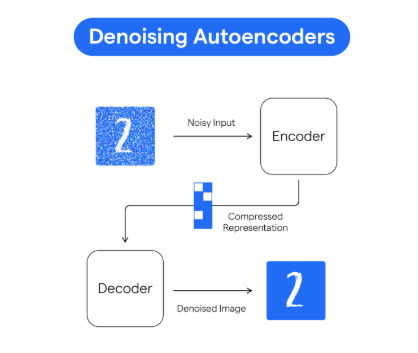
This approach helps overcome data sparsity — a common issue in collaborative filtering — by forcing the network to learn robust latent structures. Denoising autoencoders introduces random noise to inputs during training, encouraging the model to generalize rather than memorize. The result is a resilient recommender that can infer missing data points with high accuracy.
Deep Autoencoders for Collaborative Filtering
Deep Autoencoders take the basic idea of autoencoders a step further by introducing multiple hidden layers in both the encoder and decoder parts of the network. The encoder progressively compresses the high-dimensional user–item interaction matrix into a compact latent representation, capturing abstract and non-linear relationships between users and items. The decoder then attempts to reconstruct the original interaction matrix from this compressed representation, essentially predicting how users would rate unseen items.
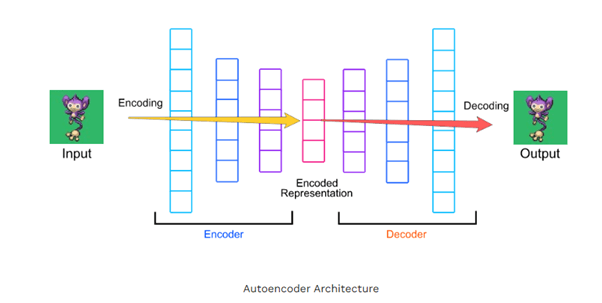
This architecture allows the model to uncover deeper structures in the data compared to shallow models. For example, while a simple autoencoder might only capture basic preference similarities, a deep version can model hierarchical patterns — such as genre preferences, actor influence, or temporal shifts in user behavior. During training, the network minimizes the reconstruction loss (commonly mean squared error) between the predicted and actual ratings, thereby learning robust embeddings that reflect users’ intrinsic tastes.
Deep autoencoders are particularly effective for explicit feedback datasets like movie or product ratings, where the numerical value of the rating carries rich information. They can also be extended for implicit feedback (like clicks or views) using different loss functions such as binary cross-entropy. In essence, deep autoencoders generalize the concept of matrix factorization but with non-linear transformations, enabling them to capture more complex interactions and deliver highly personalized recommendations.
Module 3: Deep Learning for Recommendations
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
