Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
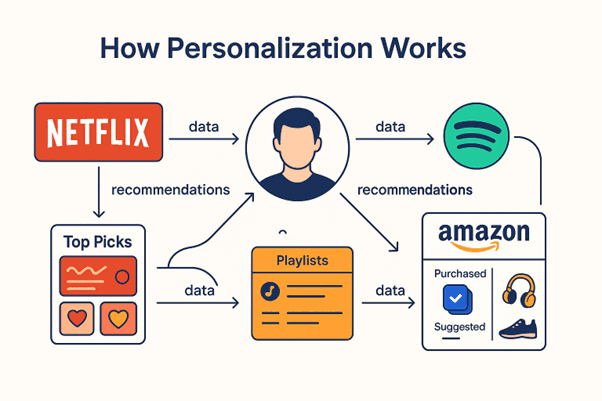
How Recommendation Systems Work
Last Updated: 29th January, 2026We’ve all experienced the magic of opening an app and finding exactly what we wanted — sometimes even before we searched for it. Behind this magic, a Recommendation System processes millions of data points and predicts what you might like next, based on what it has learned about you and other users.
The Core Idea
At its heart, a recommender system is a mapping function:
It estimates how much a user will like a particular item.
Higher scores indicate a stronger likelihood of recommendation.
User-Item Interaction Matrix
All recommendation systems begin with a User–Item Matrix:
| User | Movie A | Movie B | Movie C | Movie D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 5 | 4 | ? | ? |
| U2 | 3 | ? | 4 | 2 |
| U3 | ? | 5 | 5 | ? |
Rows = users
Columns = items
Values = explicit ratings or implicit behaviors
“?” = unknown ratings that the system needs to predict
The goal is to fill in these missing values to make personalized recommendations.
The Learning Process
Recommendation systems follow a machine learning pipeline:
Data Collection → Gather historical interactions (clicks, purchases, likes).
Preprocessing → Handle missing values, encode users/items numerically.
Pattern Extraction → Find similarities or learn embeddings.
Prediction → Estimate unseen ratings or generate rankings.
Evaluation → Compare recommendations against actual user behavior to refine the model.
Example: Simple Matrix-Based Recommendation
import pandas as pd import numpy as np ratings = pd.DataFrame({ 'User': ['U1', 'U1', 'U2', 'U2', 'U3', 'U3'], 'Movie': ['A', 'B', 'A', 'C', 'B', 'C'], 'Rating': [5, 4, 3, 4, 5, 5] }) # Pivot the data to create a user-item matrix matrix = ratings.pivot_table(index='User', columns='Movie', values='Rating') print("User-Item Rating Matrix:\n", matrix.fillna(0))
Output:
Movie A B C User U1 5.0 4.0 0.0 U2 3.0 0.0 4.0 U3 0.0 5.0 5.0
Each row captures a user’s behavior pattern.
Missing entries (0.0) are where the system predicts new preferences.
Model Objectives
The recommender’s main goal is to predict missing ratings as accurately as possible. Methods include:
Collaborative Filtering → based on similar users
Content-Based Filtering → based on item features
Matrix Factorization → discovers latent factors
Neural Networks / Deep Learning → learns complex patterns
Graphical Representation – Recommendation Pipeline
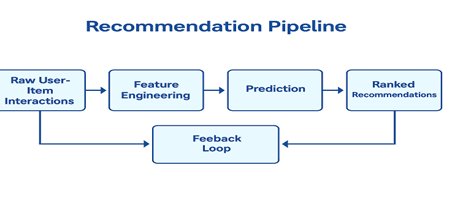
Captures the end-to-end workflow from raw data to personalized output.
Real-World Example – Spotify
Tracks listening history, skips, playlist additions, and even the time of day a user listens.
Builds embeddings representing your musical fingerprint.
Recommends songs whose embeddings are closest to yours in vector space.
Key Takeaways
Recommenders predict missing user-item interactions.
Data is represented as a matrix of ratings or behaviors.
The system learns patterns, predicts scores, and continuously refines results.
Collaborative, content-based, or hybrid models can be applied depending on the use case.
Module 1: Introduction to Recommendation Systems
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
