Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF)
Last Updated: 29th January, 2026As data grows in scale and complexity, traditional recommendation techniques — such as content-based or collaborative filtering — often struggle to capture nonlinear relationships, contextual dependencies, and dynamic user preferences. Deep Learning has transformed this landscape by enabling models to automatically learn abstract, high-dimensional representations of users and items.
This module introduces neural architectures that power today’s most advanced recommenders — from Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF) to Autoencoders and Sequence-based models like RNNs and LSTMs.
Concept & Architecture
Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF) replaces the linear operations of traditional matrix factorization with neural networks that learn nonlinear user–item interactions. Instead of representing users and items as static latent vectors, NCF feeds these embeddings into a multilayer perceptron (MLP) that captures complex relationships.
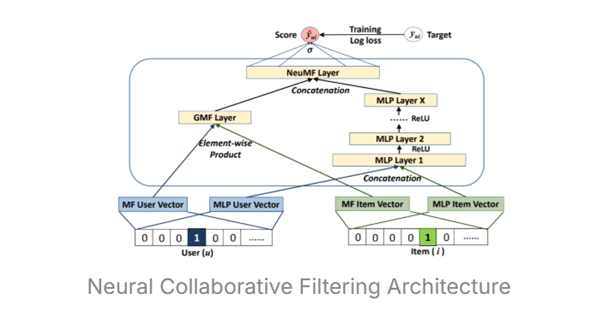
At a high level, each user and item is represented as an embedding vector learned during training. These embeddings are concatenated or multiplied and passed through multiple dense layers with nonlinear activation functions (like ReLU). The final layer outputs a predicted preference score — for example, how likely a user is to watch a movie or click a product. NCF models are trained using loss functions such as binary cross-entropy (for implicit feedback) or mean squared error (for explicit ratings).
This flexibility allows NCF to capture higher-order dependencies that linear models miss. It forms the foundation for deep recommender systems deployed by platforms like YouTube and TikTok, which rely heavily on neural embeddings and layered architectures for personalization at scale.
Implementation using Keras
Implementing NCF in Keras is straightforward due to its modular design. We begin by creating separate embedding layers for users and items. These embeddings are flattened, concatenated, and passed through several dense layers that progressively learn abstract interaction patterns.
A simple Keras implementation might look like this:
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Embedding, Flatten, Concatenate, Dense num_users, num_items, latent_dim = 1000, 1500, 8 user_input = Input(shape=(1,)) item_input = Input(shape=(1,)) user_emb = Embedding(num_users, latent_dim)(user_input) item_emb = Embedding(num_items, latent_dim)(item_input) merged = Concatenate()([Flatten()(user_emb), Flatten()(item_emb)]) x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(merged) x = Dense(32, activation='relu')(x) output = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(x) model = Model([user_input, item_input], output) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy')
This model learns user–item interactions end-to-end using neural layers. By adjusting architecture depth and embedding dimensions, we can tune complexity and performance for real-world datasets.
Implementation using PyTorch
In PyTorch, NCF is implemented using its flexible class-based model definition. The process involves creating embedding layers for users and items, combining them, and passing them through fully connected layers. Training uses backpropagation with optimizers such as Adam or SGD.
Example:
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim class NCF(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_users, num_items, latent_dim): super().__init__() self.user_emb = nn.Embedding(num_users, latent_dim) self.item_emb = nn.Embedding(num_items, latent_dim) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(latent_dim*2, 64) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, 32) self.output = nn.Linear(32, 1) def forward(self, user, item): u = self.user_emb(user) i = self.item_emb(item) x = torch.cat([u, i], dim=-1) x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x)) return torch.sigmoid(self.output(x))
This neural setup mirrors the Keras version but provides more customization control — ideal for large-scale experiments or hybrid architectures. PyTorch-based recommenders are widely used in production systems for their flexibility and GPU efficiency.
Module 3: Deep Learning for Recommendations
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
