Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Types of Recommendation Systems
Last Updated: 29th January, 2026Types of Recommendation Systems
Recommendation systems are not one-size-fits-all. Based on the approach used to generate recommendations, they are broadly classified into:
Content-Based Filtering (CBF)
Collaborative Filtering (CF)
Hybrid Approaches
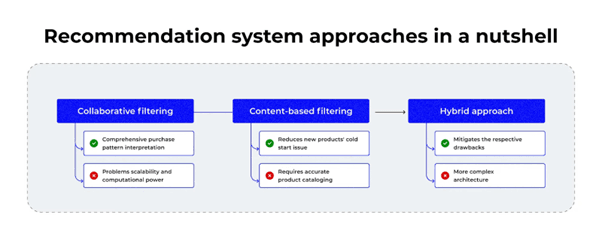
Each type has unique logic, strengths, weaknesses, and application scenarios.
Content-Based Filtering (CBF)
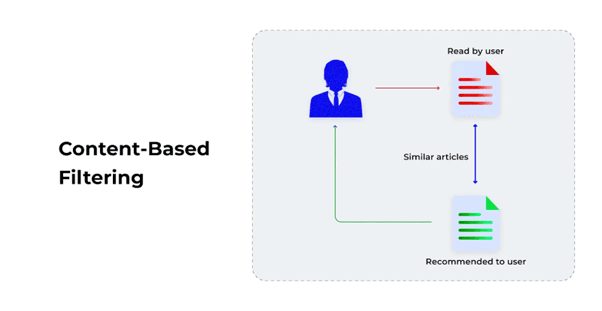
Content-Based Filtering focuses on analyzing the properties of items that a user has previously interacted with and recommending items that are similar in features.
Key Idea:
A system builds a profile for each user based on the attributes of items they like.
Recommends items with matching attributes.
Example: If a user likes “Inception” (a sci-fi, dream, action film), the system identifies other movies with similar textual or categorical features and recommends them.
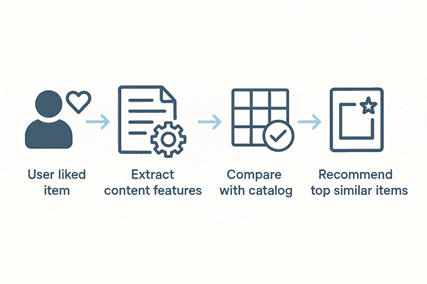
Step-by-Step Process:
1. Feature Extraction → Convert item attributes (genre, tags, keywords) into numeric vectors.
2. User Profile Creation → Aggregate features from items the user interacted with.
3. Similarity Calculation → Compare other items with user profile using similarity metrics (cosine similarity, Euclidean distance).
4. Recommendation Generation → Rank items based on similarity and recommend the top-N items.
Python Example:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity import pandas as pd # Sample movie dataset movies = pd.DataFrame({ 'Movie': ['Inception', 'Interstellar', 'Avatar', 'The Dark Knight'], 'Description': [ 'dream mind-bending sci-fi', 'space travel time black hole', 'alien world humans sci-fi', 'superhero vigilante dark city' ] }) # Convert textual features to vectors tfidf = TfidfVectorizer() tfidf_matrix = tfidf.fit_transform(movies['Description']) # Compute similarity between movies cos_sim = cosine_similarity(tfidf_matrix) # Recommend movies similar to Inception (index 0) idx = 0 similar_movies = list(enumerate(cos_sim[idx])) similar_movies = sorted(similar_movies, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[1:3] print("Movies similar to Inception:") for i, score in similar_movies: print(f"- {movies['Movie'][i]} (Similarity: {score:.2f})")
Output:
Movies similar to Inception: - Avatar (Similarity: 0.34) - Interstellar (Similarity: 0.29)
Advantages of Content-Based Filtering:
- Works for new users if item features are known.
- Recommendations are explainable, which improves user trust.
- Captures fine-grained preferences for specific item types.
Limitations:
- Limited novelty: tends to recommend very similar items repeatedly.
- Requires descriptive metadata for every item.
- Does not leverage knowledge from other users’ behaviors.

Real-World Applications:
Spotify → recommends songs based on genre, tempo, mood of previously liked songs.
Amazon → recommends products similar to what you bought before.
Netflix → suggests movies with similar genres, casts, or storylines.
Graphical Representation (Conceptual):
Collaborative Filtering (CF)
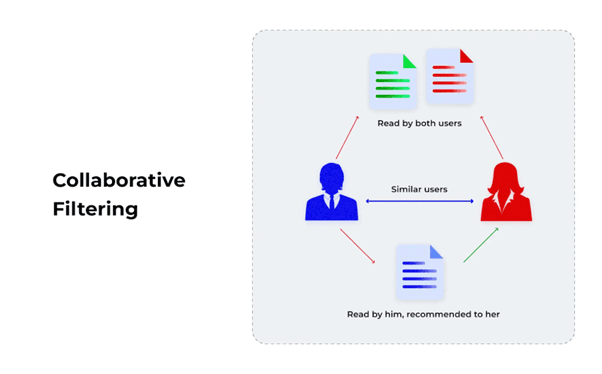
Collaborative Filtering leverages the wisdom of the crowd. It assumes that users with similar preferences in the past will like similar items in the future.
Key Idea:
CF does not require item content.
Recommendations are based on user behavior similarity or item similarity.
Types:
1. User-Based CF → find users similar to target user, recommend what they liked.
2. Item-Based CF → find items similar to those the user liked, recommend those.
Mathematical Foundation (User-Based CF):
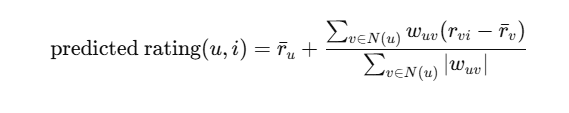

Python Example: User-Based Collaborative Filtering
import numpy as np from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity # User-Item ratings matrix ratings = np.array([ [5, 4, 0], [3, 0, 4], [0, 5, 5] ]) # Compute user similarity user_similarity = cosine_similarity(ratings) print(np.round(user_similarity, 2))
Output:
[[1. 0.73 0.66] [0.73 1. 0.72] [0.66 0.72 1. ]]
Users 1 and 2 have a similarity of 0.73, showing closely aligned preferences.
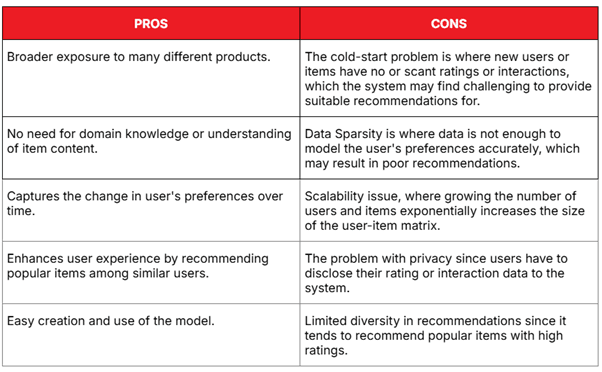
Advantages of Collaborative Filtering:
- Captures complex, hidden patterns in user behavior.
- Learn from real user interactions, independent of item features.
- Can recommend items that the user might not have discovered on their own.
Limitations:
- Cold Start Problem: new users or items have insufficient data.
- Requires a large user base and dense interactions for high accuracy.
- Sparse datasets can reduce prediction quality.
Real-World Applications:
Netflix → recommends movies liked by similar users.
YouTube → suggests videos watched by users with similar viewing patterns.
Amazon → “Customers who bought this also bought…”
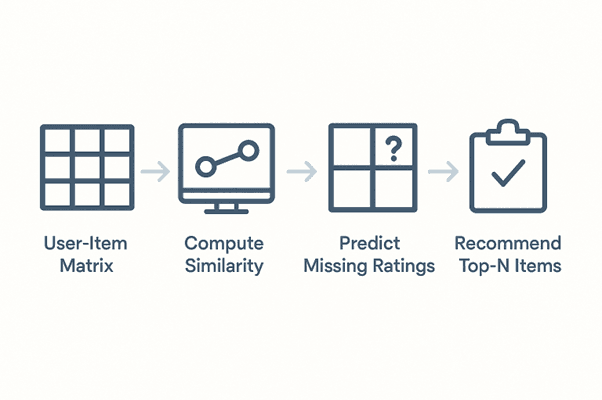
Graphical Representation (Conceptual):
Hybrid Recommendation Systems
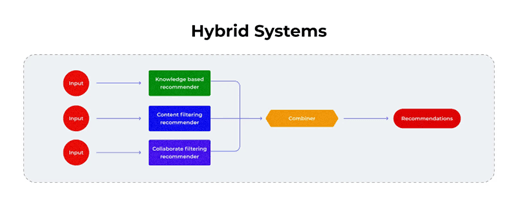
Hybrid systems combine Content-Based Filtering and Collaborative Filtering to overcome the weaknesses of each approach.
Key Idea:
Merge content features and user interaction data to generate recommendations.
Can be implemented using weighted methods, switching methods, or deep learning embeddings.
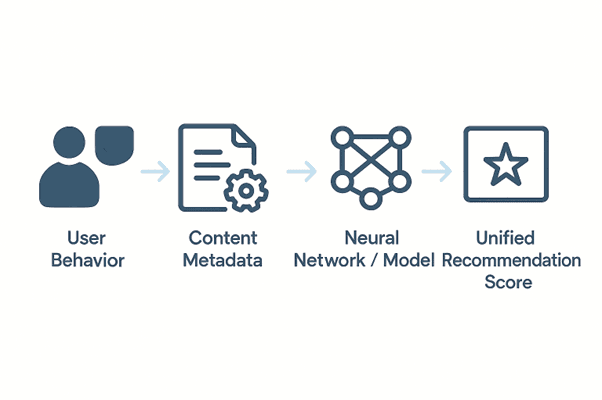
How It Works (Example – Netflix):
Content Features → genre, cast, duration, storyline keywords
Collaborative Data → user watch history, ratings, viewing habits
Model Integration → deep learning architecture merges embeddings from content and user latent vectors
Recommendation Score → unified score ranks items for recommendation
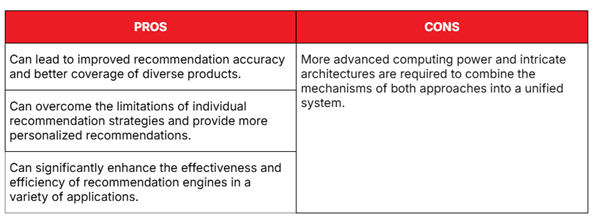
Advantages of Hybrid Systems:
- More accurate and robust recommendations.
- Mitigates cold-start problems.
- Captures both user preferences and item characteristics.
Limitations:
- Requires more computation and storage.
- Complex to design and maintain.
- Requires tuning multiple models to optimize performance.
Real-World Applications:
Netflix → blends content-based similarity with collaborative filtering from other users.
Amazon → merges product features with user purchase patterns.
Spotify → combines user listening behavior and song audio features.
Graphical Representation (Conceptual):
Module 1: Introduction to Recommendation Systems
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
