Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Building APIs for Model Serving
Last Updated: 30th January, 2026Once your model is prepared, the next step is to make it accessible to applications or users. This chapter focuses on building APIs that allow your trained model to receive input and return predictions. We will explore frameworks like Flask and FastAPI, create endpoints for real-time predictions, and discuss best practices for designing production-ready APIs. By the end, you will know how to turn your model into a fully functional, queryable service.
Why APIs are Needed
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) act as bridges between your model and the outside world. They allow applications, websites, or other services to send input data to the model and receive predictions in real time.
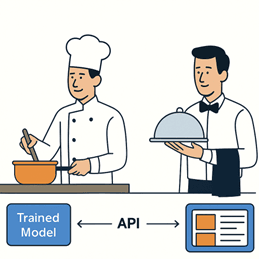
Analogy:
- Your trained model is like a chef in the kitchen.
- The API is the waiter taking orders and delivering dishes to customers.
Without an API:
- Applications cannot interact with your model efficiently.
- You cannot serve multiple users simultaneously.
- Real-time predictions are difficult or impossible.
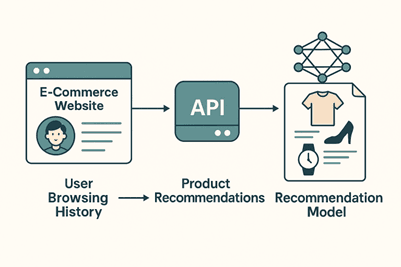
Example Scenario:
- An e-commerce website sends user browsing history to a recommendation model via an API.
- The API returns product recommendations instantly for display.
Creating a Simple API with Flask
Flask is a lightweight Python framework perfect for creating REST APIs.
Steps to Create a Flask API:
1. Install Flask:
pip install flask
2. Create a Python script (app.py):
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify import pickle app = Flask(__name__) # Load serialized model with open("model.pkl", "rb") as f: model = pickle.load(f) @app.route('/predict', methods=['POST']) def predict(): data = request.get_json() # Get input JSON data prediction = model.predict([data['features']]) return jsonify({'prediction': prediction.tolist()}) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True)
3. Run the API:
python app.py
4. Test with a POST request:
POST /predict { "features": [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2] }
Advantages of Flask:
- Simple and easy to implement.
- Widely used with strong community support.
Limitations:
By default, synchronous; may not handle very high traffic efficiently.
FastAPI for High-Performance APIs
FastAPI is designed for speed and scalability, supporting asynchronous requests and automatic documentation.
Example of FastAPI:
from fastapi import FastAPI import pickle from pydantic import BaseModel app = FastAPI() # Load model with open("model.pkl", "rb") as f: model = pickle.load(f) class InputData(BaseModel): features: list @app.post("/predict") def predict(data: InputData): prediction = model.predict([data.features]) return {"prediction": prediction.tolist()}
Advantages:
- Asynchronous support improves scalability.
- Automatic API documentation at /docs.
- Data validation ensures input is correctly formatted.
Example Use Case:
A real-time fraud detection model that must handle thousands of transactions per second.

Best Practices for API Design
1. Input Validation: Ensure the API checks input data before passing it to the model.
2. Error Handling: Return meaningful error messages for invalid requests.
3. Logging: Track requests, predictions, and errors for debugging and monitoring.
4. Versioning: Use versioned endpoints (/v1/predict) to manage updates safely.
5. Security: Use authentication, HTTPS, and data encryption for sensitive models.
Example:
Returning a clear error message:
{ "error": "Invalid input: feature vector must have 4 elements." }
Testing and Debugging Your API
Before deployment:
- Test endpoints using Postman, curl, or Python requests.
- Simulate different types of inputs, including edge cases.
- Measure response time to ensure low latency.
Example Testing with Python:
import requests url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/predict" data = {"features": [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]} response = requests.post(url, json=data) print(response.json())
Testing ensures your API is reliable, fast, and ready for production.
Summary:
- APIs make your model accessible to applications and users.
- Flask is simple and easy for small-scale APIs.
- FastAPI offers high performance, asynchronous requests, and automatic documentation.
- Best practices include input validation, error handling, logging, versioning, and security.
- Testing your API thoroughly ensures smooth and reliable deployment.
Module 3: Hands-On Model Deployment
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
