Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Understanding Model Deployment
Last Updated: 30th January, 2026In this chapter, we focus on understanding what model deployment really means and why it is critical for practical applications. We’ll explore the difference between training a model and making it production-ready, the challenges commonly faced during deployment, and the importance of serving models efficiently to users or applications. By the end of this chapter, you’ll grasp why deployment is the bridge between development and real-world impact.
What is Model Deployment?
Imagine you’ve spent weeks building a machine learning model that predicts whether a patient has a particular disease based on medical test results. Your model is accurate, robust, and tested thoroughly. It performs beautifully on your laptop, giving you predictions in seconds.
Now imagine a doctor in a hospital wants to use it to make real-time predictions for their patients. Can the doctor just open your Jupyter notebook, type commands, and run the model for every new patient? Of course not! Doing so would be inefficient, error-prone, and impossible to scale.

This is where model deployment comes in. Model deployment is the process of taking your trained model and making it accessible to users, applications, or systems in a reliable and scalable way. Deployment transforms a model from a static experiment into a practical tool that can deliver predictions in real-world scenarios.
Think of it like this:
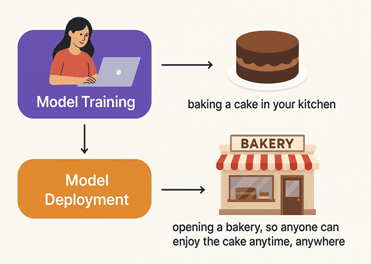
Model training is baking a cake in your kitchen. You know the recipe works and tastes amazing.
Model deployment is opening a bakery, so anyone can enjoy the cake anytime, anywhere.
Without deployment, your model remains stuck on your local machine, no matter how brilliant it is. It cannot create business impact, help users make decisions, or contribute to real-world processes.
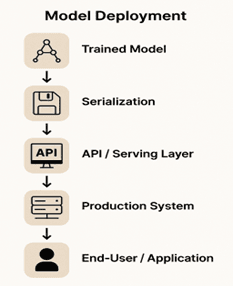
When a model is deployed, it usually goes through a series of steps:
1. Trained Model: The final version of your model, ready for inference.
2. Serialization: Saving the model in a format that can be easily loaded later, like Pickle, Joblib, or ONNX.
3. API / Serving Layer: Wrapping the model in an interface, often a REST API, so other applications or users can send input data and receive predictions.
4. Production System: Hosting the API on a server or cloud platform, ensuring it’s always available.
5. End-User / Application: The person, system, or application that requests predictions from the model.
Key Advantages of Deployment:
Accessibility: The model can be used by multiple users or systems without manual intervention.
Reliability: Predictions are consistent, fast, and accurate under different loads.
Scalability: The system can handle multiple simultaneous requests without crashing.
Monitoring: You can track model performance, detect errors, and identify data drift or concept drift.
Real-World Examples:
E-commerce: Recommendation engines suggest products based on user behavior.
Healthcare: Predictive models assist doctors with real-time diagnosis.
Finance: Fraud detection systems monitor transactions continuously, flagging suspicious activity.
Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance models alert technicians before machines fail.
Best Practices to Remember:
- Always test the model thoroughly before deployment.
- Use versioning to track updates or improvements.
- Secure APIs to protect sensitive data.
- Monitor performance and retrain models when predictions degrade over time.
In summary, model deployment is the bridge between machine learning development and real-world impact. It ensures that your model isn’t just a tool you play with on your laptop, but a practical solution that delivers value to users, systems, and businesses consistently. Deploying a model properly transforms it from a static asset into a living, working component of real-world applications.
Difference Between Training and Deployment
Building a machine learning model involves multiple stages, but two of the most critical phases are training and deployment. While they are closely connected, they serve very different purposes in the ML lifecycle. Understanding the difference is essential to bridge the gap between model development and real-world usage.
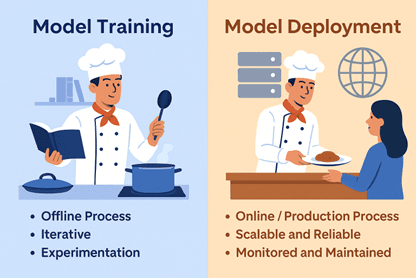
Model Training:
Model training is the process of teaching the machine learning algorithm to learn patterns from historical data. During this phase, you:
- Collect and clean data.
- Split the data into training and testing sets.
- Train a model by feeding it data and optimizing its parameters.
- Evaluate performance using metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, or RMSE.

Think of training as preparing a chef in the kitchen. The chef learns the recipe, practices cooking it perfectly, and refines the technique until it consistently produces great results.
Key characteristics of training:
Offline Process: Training happens on historical data, usually on your local machine or a dedicated training server.
Iterative: You may need multiple iterations, tuning hyperparameters, testing different algorithms, or adding more data.
Experimentation: Training is a learning and testing phase; the model may not be ready for production yet.
Model Deployment:
Deployment is the next step after training. It’s about taking the trained model and making it available for real-world use. In this phase, you:
- Serialize the model (save it in a reusable format).
- Wrap it in a service or API so it can accept input and return predictions.
- Host it on a server, cloud platform, or edge device for real-time or batch usage.
- Monitor performance, handle errors, and ensure it scales with demand.
Continuing the chef analogy, deployment is opening the restaurant. The chef is now serving real customers, taking orders, and delivering dishes consistently. Customers experience the recipe in real life, and the chef’s skills create real impact.
Key characteristics of deployment:
Online / Production Process: Deployment makes the model accessible to applications, users, or systems.
Scalable and Reliable: Handles multiple requests simultaneously without errors.
Monitored and Maintained: Ensures the model continues to perform well over time.
Major Differences Between Training and Deployment:
| Aspect | Training | Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Learn patterns from data | Serve predictions in real-world scenarios |
| Environment | Local machines, notebooks, or training servers | Production server, cloud, or edge devices |
| Nature | Offline, experimental | Online, operational |
| Users | Data scientists / ML engineers | End-users, applications, systems |
| Focus | Accuracy, optimization, experimentation | Reliability, scalability, accessibility |
Why Understanding the Difference Matters:
Many beginners assume that building a good model is enough. But a highly accurate model that is never deployed is essentially useless in practice. Deployment ensures that the model’s predictions reach the people, systems, or processes that need them, creating real-world value.
In real scenarios:
- A trained fraud detection model that is never deployed cannot prevent financial loss.
- A recommendation system that stays in a notebook cannot suggest products to users in real time.
Properly separating training and deployment phases also allows versioning, testing, and maintenance without disrupting live systems.
Summary:
- Training and deployment are two distinct but complementary stages of the ML lifecycle.
- Training focuses on learning from historical data, experimentation, and achieving high accuracy.
- Deployment focuses on serving predictions reliably, efficiently, and at scale to end-users or systems.
- Understanding this difference is crucial for building ML solutions that not only work well but also create real-world impact.
Deployment Challenges
Deploying a machine learning model may sound straightforward — train a model, wrap it in an API, and make it available for use. However, in reality, deployment comes with several challenges that must be addressed to ensure the model works reliably in production. Understanding these challenges is essential for creating robust, scalable, and maintainable ML solutions.
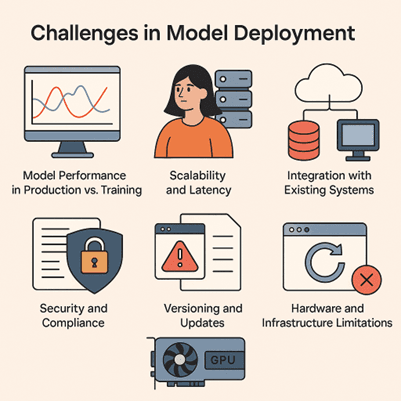
1. Model Performance in Production vs. Training
A model that performs exceptionally well on historical or test data may not always perform the same way in production. This is often due to:
Data drift: When the distribution of incoming data changes over time compared to the training data.
Concept drift: When the underlying relationships in the data evolve, making previous patterns less accurate.
For example, a model predicting customer churn trained on last year’s data may fail if user behavior changes significantly this year. Continuous monitoring and periodic retraining are essential to maintain accuracy.
2. Scalability and Latency
A deployed model must handle multiple simultaneous requests efficiently, often from thousands or millions of users. Common challenges include:
- Ensuring low latency so predictions are returned quickly.
- Designing the system to scale horizontally (adding more servers) or vertically (using more powerful machines).
- Managing resource constraints, especially for computationally heavy models like deep learning networks.
If scalability is not considered, the system may become slow, fail under high load, or crash entirely.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Models rarely operate in isolation. They must integrate seamlessly with existing applications, databases, or cloud services. Challenges include:
- Designing APIs that are compatible with multiple client systems.
- Ensuring secure and efficient data pipelines.
- Handling edge cases, missing data, or unusual input formats gracefully.
Poor integration can render even the most accurate models unusable in practice.
4. Monitoring and Maintenance
Deployment is not a one-time activity. Models require continuous monitoring to ensure:
- They provide accurate predictions over time.
- Errors, downtime, or unexpected behavior are detected quickly.
- Retraining or updates are applied when performance degrades.
Without monitoring, issues may go unnoticed, leading to incorrect predictions and potential business losses.
5. Security and Compliance
When models handle sensitive data — like medical records, financial transactions, or personal user information — security is paramount. Deployment challenges include:
- Protecting APIs against unauthorized access or attacks.
- Ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Encrypting data in transit and at rest to prevent breaches.
Failing to address these concerns can result in serious legal, ethical, and financial consequences.
6. Versioning and Updates
Models evolve over time, and new versions may need to replace old ones without disrupting service. Challenges include:
- Managing multiple model versions simultaneously.
- Ensuring backward compatibility for applications relying on predictions.
- Testing new versions thoroughly before deployment.
Proper versioning strategies help maintain system stability and minimize downtime during updates.
7. Hardware and Infrastructure Limitations
Some models, especially deep learning models, require high computational power, GPUs, or specialized hardware. Deployment challenges include:
- Ensuring the infrastructure supports model requirements.
- Optimizing model size and inference speed for constrained environments (e.g., mobile or edge devices).
Summary:
Deploying a machine learning model is far more than just exposing it via an API. Key challenges include:
- Performance differences between training and production (data drift, concept drift).
- Scalability and low-latency predictions.
- Integration with existing systems and handling diverse data.
- Continuous monitoring, maintenance, and retraining.
- Security, compliance, and data privacy concerns.
- Versioning and smooth updates.
- Infrastructure and hardware limitations.
Addressing these challenges is critical to ensure that your model not only works but also provides reliable, scalable, and secure predictions in the real world.
Module 1: Fundamentals of Model Deployment
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
